EXPLORATION
Exploring Mars and Beyond: From Red Planet Dreams to Interplanetary Solutions

Mustafa syed ahmed
October 12th, 2023
Mars, often referred to as the "Red Planet," has held a special place in humanity's imagination for centuries. It's a world of mystery, beckoning us with the promise of adventure and discovery. The fascination with Mars has fueled exploration efforts led by scientists, engineers, and space enthusiasts from around the world. In this comprehensive article, we will embark on a journey to uncover the challenges and opportunities that await us in our quest to explore and eventually colonize the enigmatic Red Planet.
The Beginning Of The Mars Project
The dream of exploring Mars has long been a driving force for space agencies and private companies alike. NASA's ambitious "Journey to Mars" initiative, launched in the early 2010s, marked a significant milestone in human space exploration. This initiative aimed to develop the necessary technologies and strategies to send astronauts to Mars by the 2030s. Notably, SpaceX, founded by visionary entrepreneur Elon Musk, has played a pivotal role in advancing our understanding of Mars.
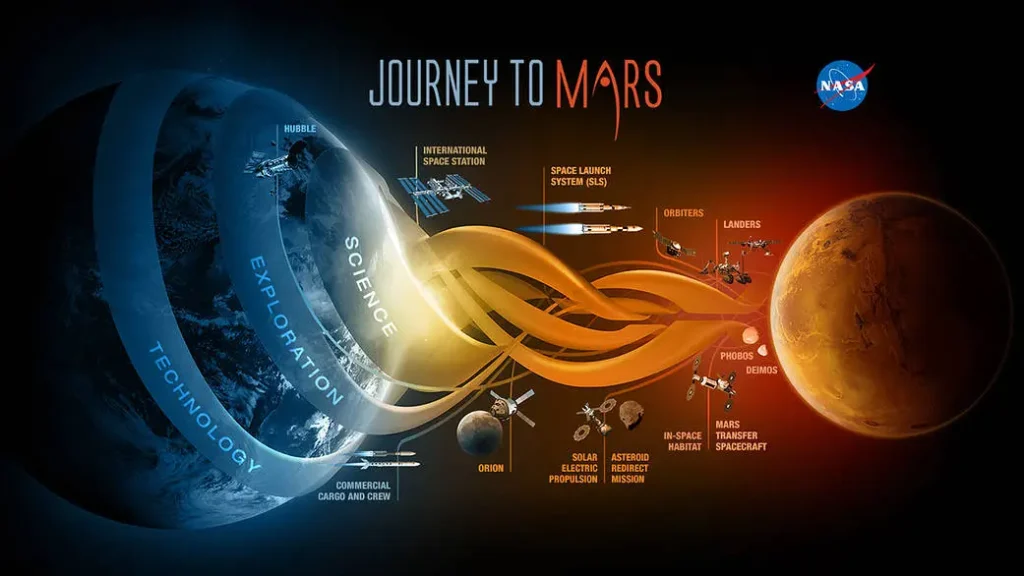
The image portrays NASA's ambitious project, which aims to pave the way for human missions to both Mars and an asteroid. These missions are in alignment with the goals outlined in the bipartisan NASA Authorization Act of 2010 and the U.S. National Space Policy, both of which were issued in the same year.
Elon Musk's audacious vision of creating a multi-planetary society led to the birth of the "Mars Colonial Transporter" (MCT) project, later rebranded as "Starship." SpaceX's relentless pursuit of a fully reusable spacecraft has brought us closer to the realization of Mars colonization. With an estimated investment of approximately $5 billion in the project, SpaceX is committed to establishing a self-sustaining colony on Mars.
The Journey to Mars: Challenges and Opportunities
Embarking on a journey to Mars is no small feat. The Red Planet resides millions of miles away from Earth, presenting a myriad of challenges. The journey itself spans six to eight months, with spacecraft navigating through deep space while contending with the perils of radiation and space debris. However, these very challenges are the crucible of innovation and technological advancement.
Landing on Mars poses another set of technical challenges. The planet's thin atmosphere and weaker gravity compared to Earth require precise landing maneuvers. Overcoming these obstacles necessitates meticulous planning and engineering expertise. Successfully landing on Mars opens the door to scientific exploration and the potential discovery of ancient life forms.
Scientific Discovery and Exploration

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover took 62 individual images with its WATSON camera, on April 6, 2021 (Photo Credit: NASA)
At the heart of Mars exploration lies the pursuit of scientific discovery. Mars is a treasure trove of geological and environmental data that can provide insights into the history of our own planet and the possibility of extraterrestrial life. Robotic missions, exemplified by NASA's Curiosity and Perseverance rovers, have already yielded invaluable information about Mars' geology, atmosphere, and potential for past microbial life.
Future missions are poised to build upon these discoveries, delving deeper into the mysteries of Mars. Scientists aspire to unearth more evidence of Mars' past habitability and gain a comprehensive understanding of its potential to support human life. Through the study of Mars, we may glean insights into the origins of life, planetary evolution, and the prospects of habitable environments beyond Earth.
Colonizing the Red Planet
The vision of colonizing Mars has captured the imagination of scientists and space enthusiasts worldwide. The creation of a self-sufficient colony on Mars is viewed as a pivotal step in ensuring the long-term survival of humanity. SpaceX envisions a future where settlers gradually establish a self-sustaining society on Mars, leveraging the planet's resources to sustain human life.
Colonization is rife with challenges, encompassing radiation protection, resource utilization, and environmental factors. The harsh Martian environment demands the development of advanced life support systems, habitat structures, and technologies for resource extraction and utilization. However, with each challenge comes an opportunity for innovation and the potential for groundbreaking discoveries.
This image serves as a powerful visual representation of the contrast between our home planet and the potential future of Martian colonization (Photo Credit: SpaceX and NASA)
Resource Utilization and Sustainability
Central to Mars colonization is the utilization of local resources. Mars offers a wealth of resources that can be harnessed to support human life and foster self-sufficiency. Water, in the form of ice, can be extracted from Martian soil, serving as a source for drinking, agriculture, and oxygen production. Furthermore, the carbon dioxide-rich Martian atmosphere can be converted into breathable air through advanced technologies.
Harnessing Martian resources diminishes reliance on Earth for supplies and lays the groundwork for sustainable colonization. It also provides insights into resource utilization techniques that may be applied to our home planet, addressing global challenges related to resource scarcity and environmental sustainability.
The exploration and colonization of Mars necessitate international cooperation. Space agencies like NASA, ESA, and Roscosmos have joined forces to pool resources, expertise, and funding for Mars missions. Collaborative endeavors enable shared costs, diverse perspectives, and increased prospects of success.
NASA's Artemis program, designed to establish sustainable lunar exploration as a stepping stone to Mars, exemplifies this spirit of collaboration. The program engages international partners, including the European Space Agency (ESA) and commercial space enterprises. By working collectively, we can leverage collective knowledge and resources to surmount the challenges of Mars exploration and pave the way for future human missions.
The Future of Humanity
The pursuit of Mars exploration and colonization transcends scientific curiosity; it pertains to the future of humanity. As we grapple with challenges such as climate change and the finite resources of Earth, the imperative of becoming a multi-planetary species becomes increasingly evident. Mars offers the potential of a second home, a contingency plan to secure our species against unforeseen catastrophes.
By exploring Mars, we expand the frontiers of our understanding of the universe and our place within it. We push the boundaries of human knowledge and technological capabilities, inspiring future generations to pursue careers in science and engineering. The journey to Mars epitomizes our indomitable spirit of exploration and our commitment to stretching the limits of what is achievable.
Financing the Martian Dream
A pressing question arises: Who will fund this grand endeavor? Government organizations like NASA, while historic pioneers of space exploration, are no longer in their heyday, with funding levels far from their peak during the moon missions. On the other hand, private corporations such as SpaceX offer promise. However, shareholders ultimately influence these companies' decisions. Without a guaranteed profit from Martian ventures, it's uncertain whether billions of dollars will be committed to the project. Moreover, doubts persist regarding the practicality of the technologies proposed to address Mars's unique challenges. Many of these technologies, while holding great promise, remain experimental and costly. Ensuring their effectiveness and affordability is a significant hurdle.
Unresolved Martian Mysteries
Beyond financial and technological considerations, several enigmas about the Martian environment remain unsolved. The low gravity on Mars potentially has adverse effects on human health, including muscle atrophy and bone demineralization. Frequent, massive dust storms on Mars can block sunlight for weeks, posing significant challenges for colonists, particularly in terms of food production and energy generation. Furthermore, Mars's weak magnetosphere and thin atmosphere allow dangerous levels of ionizing radiation to reach the surface, threatening infrastructure, technology, and human health. Another aspect that cannot be overlooked is the psychological and social impact of living on Mars, especially during the early missions. Prolonged isolation, repetitive tasks, and cramped living conditions could lead to serious psychological effects on the crew, which necessitates thoughtful consideration and planning.
Terraforming Mars: A Contemplated Solution
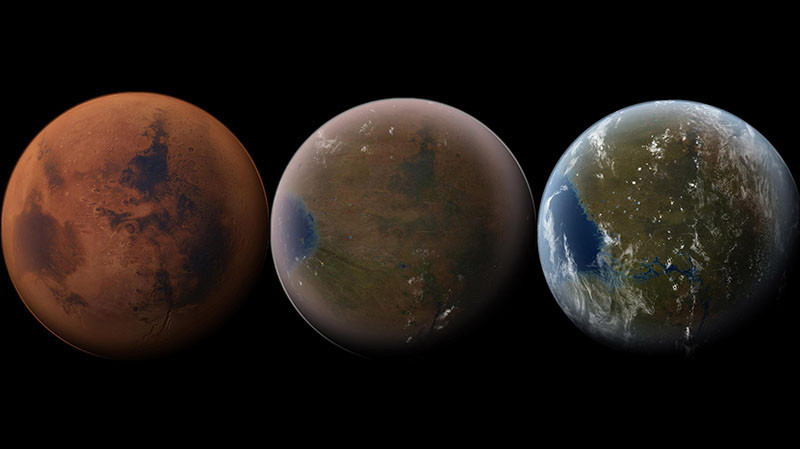

Artist’s impression of the terraforming of Mars, from its current state to a earth like world. (Photo Credit: Daein Ballard)
Astrophysicist Neil deGrasse Tyson once remarked,
"If you want to ship a billion people to Mars and have them live there as they are living on Earth , you'll have to terraform Mars."
Terraforming, a hypothetical process of intentionally altering Mars's atmosphere, temperature, surface, and ecology to resemble Earth's, emerges as a long-term solution. In the distant future, when substantial numbers of humans potentially inhabit Mars, constructing specially designed infrastructure, water recovery systems, and more might become infeasible. Instead, albeit with a higher initial investment, terraforming could transform Mars into a habitable environment, eliminating the need for specialized equipment.
Balancing Aspiration and Responsibility
In conclusion, the vision of colonizing Mars is an ambitious and alluring endeavor that sparks the imagination of people worldwide. While the path ahead is filled with challenges, the prospects for scientific discoveries, technological innovations, and the enduring survival of humanity are immense. Through international collaboration, resource utilization, and sustainable practices, we can unravel the mysteries of Mars and inch closer to becoming a multi-planetary species.
However, it is essential to remember that rather than using Mars as an escape from Earth's challenges, our foremost responsibility is to address those challenges here at home. Solutions to issues like climate change, alternative energy sources, and sustainable technologies should be our primary focus. Only by healing and preserving our Earth can we expand and prosper as a species, continually extending the boundaries of human exploration and understanding.
"The universe is under no obligation to make sense to you. And in the face of this, we explore, and we prevail."- Neil deGrasse Tyson
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Receive amazing space news and stories that are hot off the press and ready to be read by thousands of people all around the world.
